How does it work?
The idea behind Early Logic is a regular diagnosis of mathematical competence and adjusting the possible therapy to the needs of your child, which significantly helps the child to achieve better learning results.

The idea behind Early Logic is a regular diagnosis of mathematical competence and adjusting the possible therapy to the needs of your child, which significantly helps the child to achieve better learning results.


The full diagnosis includes the evaluation of a possible risk of dyscalculia
and is made on the basis of a detailed report regarding the child.
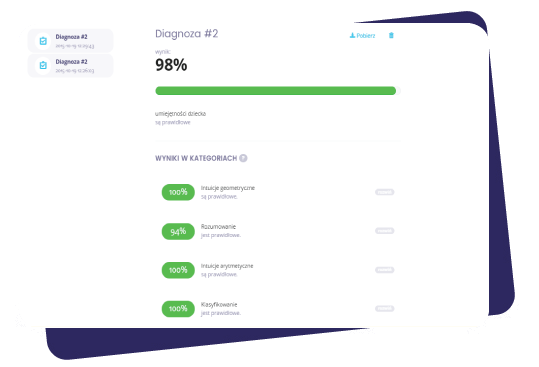
This report is made after the child solves 120 exercises from the selected level.
The diagnostic suite of EarlyLogic consists of 7 applications dedicated to children
aged 4-9 (three applications for kindergarten children aged 4-6,
and four applications for primary school children aged 6-9).
Each application includes 120 carefully selected exercises.
The applications can be used multiple times because new exercises are generated upon each use.
Individual test results (a report), in which parents or teachers can find quantitative
(percentage results) and qualitative (pedagogical diagnosis) information are included in the
product.
The pedagogical diagnosis will include the evaluation of the risk level of dyscalculia,
or information about the lack of such risk, with emphasis on the areas that require therapeutical
actions.}